AI Fundamentals: How to Define Artificial Intelligence
One of the biggest obstacles to understanding, agreeing upon & harnessing the potential of AI is in understanding it plainly. How to understand it one term at a time.
If we can’t speak plainly, clearly and understand one another, the task of using AI, or regulating its development will be rendered impossible.
Neuroscientist/policy researcher Joseph Keller wrote plainly about this issue recently. “It is imperative that we not only know what we are talking about regarding AI, but agree on how we talk about it,” he says.
It’s an issue that comes up a lot when I speak with families about AI and the impact it will have on their lives and those of their children: with no clear consensus on the lexicon, how do we move forward productively?
So instead of nodding our heads with a “note to self” to figure it all out “later” let’s dig into what we do know today…
Understanding is Doing
The short glossary below is an effort to help us keep focused on the basics. The ability to understand comes, of course, from doing. And from talking to our neighbors, families, co-workers, and friends.
This is a work-in-progress that I’ll update as needed. I add some of my definitions and editorializing of these ideas, but all words are hyperlinked to a more sophisticated definition as well. If you have any questions, ideas, or words you want to dig into, please let me know.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the “big tent” concept here. It is defined as technology that enables computers and machines to simulate/replicate human intelligence. AI is both complicated (i.e., in the sheer breadth of what is possible) and incredibly simple (i.e., we can all envision ways to “replicate” our thoughts and behavior).
I find it easiest to think of AI as a simple formula: data (mostly our data) + “math” (the computer algorithms used to process the data) + the computing power (chips, storage, energy) = “innovation” that can do what our brains do…solve problems, answer questions, analyze data and do rote activities.
If you think of the concept as “anything humans can do” in the broadest terms, you can see the breadth and scope of possibility with AI innovation. Here are some specific terms you might have come across already.
Artificial General Intelligence » This is used to refer to AI that is, essentially, smarter than us. We’re not there yet, but it’s a very important concept as it’s both ill-defined, but also considered the “holy grail” of where companies are off racing to.
Algorithm » This is the set of rules that a machine follows to learn how to do a task. They are specific to the company/organization/person developing AI innovation.
Deep Learning » This field is part of machine learning and focuses on the learning of complex patterns.
Generative AI » Exactly as it sounds, generative AI allows users to “create” something, image AI is a great example.
Machine Learning » This term is more intuitive than most: this is the field within AI where machines, well, learn. So, it’s the math behind AI.
Large Language Models (LLM)
Our day-to-day understanding of AI right now is generally LLMs. Again, it’s exactly as it seems: large amounts of sequential data, mostly text based, that is processed and turned into a response prompted by a user’s question.
Chatbot (also Conversational AI) » A computer program designed to simulate human conversation through text or voice interactions.
ChatGPT » While there are now several competitors, the fervor of the past year + came after the launch of ChatGPT.
Hallucinate/Hallucination » In a nutshell, this is when the answer a user receives is inaccurate despite the confidence in its response.
Affective Computing
Affective computing is also known as emotion AI (or emotional AI), is a technology that seeks to identify, process, and simulate our feelings. It’s a hybrid of computer science, psychology, and cognitive science. And, as mentioned above, while all the terms here are inter-related with AI, I’m isolating this area of computing for its interrelatedness to other fields and its implications in practice.
Sentiment analysis » The ability to process written data and “interpret” for a user’s “sentiment” toward an issue, topic, brand, etc. is not new per se. But now as AI advances we are talking about the overlay of voice (intonation), facial movements and other visual aspects to determine sentiment.
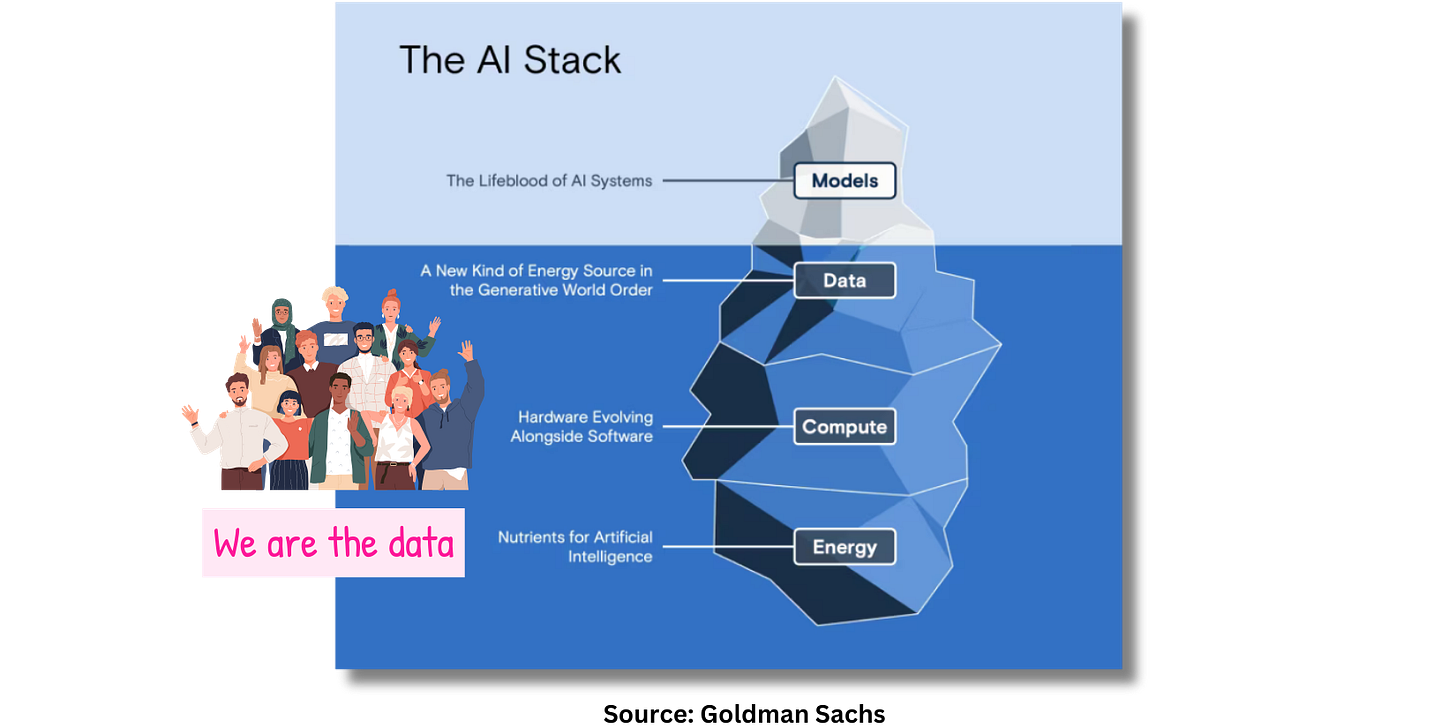
Data
Data, of course, underpins all of this. It is the “fuel” of AI. But we should be very specific and clear about how we talk about and understand data because of the profound impact it has (and will continue to have in larger measure) on our privacy.
Data Science » Data science is a field of study that uses statistics, computer science, and information science to analyze data and solve problems.
Big Data » These are large sets of data used for projects such as creating AI innovation.
Specific to AI, there are terms that often belie the greater impact on all of us in their simplicity. Because to create AI innovation means to “train” AI tools and systems. And that data comes from all of us.
Training Data » The dataset used to train a machine learning model.
Pre-Trained Data » Think of this like building blocks to that go into the AI model/tool that a developer wants to create. You’ll see this as an offering typically from enterprise businesses, such as Amazon Web Services.
How Others Define AI
For the past couple of years, I’ve been collecting links to pages where corporations, universities, and governments define AI. I find it a helpful resource and a great way to look at the bigger picture in how we approach understanding this space. Here is a list that I continue to update. It’s interesting context for the different ways in which AI is defined and communicated.
Government
About Artificial Intelligence, The National AI Research Resource Task Force
Select Committee on Artificial Intelligence, White House
Artificial Intelligence, U.S. Department of State
Intelligence Overview, U.S. Department of Commerce (National Institute of Standards and Technology
DOE Explains… Artificial Intelligence, U.S. Department of Energy
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Applying Advanced Tools for Public Health, CDC
Artificial Intelligence, National Institutes of Health
Artificial Intelligence, Department of Defense
The Birth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) Research, Lawrence Livermore Labs
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, United States Agency for International Development
Science 101: Artificial Intelligence, Argonne National Laboratory
Artificial Intelligence (AI), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)
What is artificial intelligence, and how is it used? | Topics, European Parliament
Industry
What is Artificial Intelligence, Accenture
What is Artificial Intelligence, Amazon
Artificial Intelligence, Cisco
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?, Cloudflare
What is Artificial Intelligence, General Electric
What is Artificial Intelligence, Google Cloud
How Artificial Intelligence is Accelerating Innovation in Healthcare, Goldman Sachs
What is Artificial Intelligence, Hewlett Packard
What is Artificial Intelligence, IBM
What is Generative AI?, McKinsey
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning, Microsoft
What is Artificial Intelligence, Oracle
What is Artificial Intelligence, SAP
Artificial Intelligence: What it is and Why it Matters, SAS
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, UBS
What Every CEO Should Know about Generative AI, McKinsey
Academia
Exploring New Frontiers in AI, University of Penn
What is AI, Britannica
History of Artificial Intelligence, Harvard
Artificial Intelligence Overview, MIT Technology Review
Machine Learning Explained, MIT
What is AI, CalTech
Artificial Intelligence Definitions, Stanford
An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence, University of Cincinnati
Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning: What’s the Difference?, Northeastern University
How Do Businesses Use Artificial Intelligence? - Wharton Online, University of Pennsylvania
Advances in Artificial Intelligence for Infectious-Disease, New England Journal of Medicine
Artificial intelligence Definition & Meaning, Merriam-Webster
Think Tanks & NGOs
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?, Council on Foreign Relations
Artificial Intelligence, The Royal Society
Artificial Intelligence, UNESCO
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Humans, Pew Research
Artificial Intelligence The Rise Of The Intelligent Machine, American Alliance of Museums
What is Artificial Intelligence, Brookings Institute
What is Artificial Intelligence, World Economic Forum
Artificial intelligence, Wikipedia
Media
Artificial Intelligence is Permeating Business at Last, The Economist
A simple Guide to the Expansive World of Artificial Intelligence, Popular Science
Artificial Intelligence News, Wired
How Can an A.I. Learn to Write? Choose a Famous Author, and We’ll Show You, New York Times
Artificial Intelligence, New Scientist
Artificial Intelligence, The Guardian
Leveraging AI to Advance the Power of Facts, Associated Press
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Employment, Wall Street Journal
Not everything we call AI is actually artificial intelligence, The Conversation
What Will Our Society Look Like When Artificial Intelligence, Smithsonian Magazine
Why Artificial Intelligence Needs to Understand Consequences, Nature Journal
What is AI? Everything to know about artificial intelligence, ZDNet